Investing in index ETF is one of the easiest way to gain diversification with low fees. And there are so many different types of index ETFs. In this article, we will be doing a comparison between these 2 popular ETFs: VUG vs VTI.
The main difference between VUG vs VTI is, VUG consist of only large cap companies that falls under the Growth category in the US market. VTI, on the other hand, is consist of a companies of all different cap ranging from micro to mega cap in the US. This include companies of different characteristics including growth companies.
Read on for a more comprehensive coverage.
An Overview of VUG vs VTI
| Vanguard Growth ETF (VUG) | Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Benchmark Index | CRSP US Large Cap Growth Index | CRSP US Total Market Index |
| Expense Ratio | 0.04% | 0.03% |
| Number of Stocks | 253 | 3,992 |
| % of 10 largest holdings | 41.36% | 22.22% |
| Dividend Yield | 0.77% | 1.65% |
Source: advisors.vanguard.com
VUG tracks the CRSP US Large Cap Growth Index. The CRSP US Large Cap Growth Index classifies growth companies using the future long-term and short-term growth in EPS (Earnings per shares), 3-year historical growth in EPS, 3-year historical growth in sales per share, current investment-to-assets ratio, and return on assets.
VTI tracks the CRSP US Total Market Index. This index comprises of US companies across mega, large, small and micro caps.
This is why we see a stark difference in the number of stocks that these funds hold.
Vanguard funds are known for their low cost ETF. Both these ETFs rock at their nearly identical expense ratio with the Vanguard Growth ETF at 0.04% and Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF at 0.03%. This means that for every $10,000 you invest, you are only paying $4 and $3 respectively each year in management expenses.
The dividend yield for the Total Stock Market ETF (1.65%) is higher than that of Growth ETF (0.77%). This is expected because VUG consist of Growth companies. Growth companies usually retain their a large portion of their earnings for company growth and expansion, instead of distributing it to shareholder as dividend.
FUND COMPOSITE VUG vs VTI
Market Capitalization
| Market Size | Vanguard Growth ETF (VUG) | Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) |
|---|---|---|
| Large | 82.3% | 68.5% |
| Medium/Large | 4.5% | 4.3% |
| Medium | 11.6% | 13.4% |
| Medium/Small | 1.6% | 6.1% |
| Small | 0.0% | 7.7% |
Source: advisors.vanguard.com
Top 10 Holdings
| Vanguard Growth ETF (VUG) | Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) |
|---|---|
| Apple Inc. (AAPL) 12.52% | Apple Inc. (AAPL) 12.52% |
| Microsoft Corp. (MSFT) 11.39% | Microsoft Corp. (MSFT) 11.39% |
| Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN) 4.64% | Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN) 4.64% |
| Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL) 3.36% | Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL) 3.36% |
| Alphabet Inc. (GOOG) 2.93% | Alphabet Inc. (GOOG) 2.93% |
| NVIDIA Corp. (NVDA) 2.18% | NVIDIA Corp. (NVDA) 2.18% |
| Tesla Inc. (TSLA) 2.11% | Tesla Inc. (TSLA) 2.11% |
| Visa Inc. (V) 2.09% | Visa Inc. (V) 2.09% |
| Home Depot Inc. (HD) 2.05% | Home Depot Inc. (HD) 2.05% |
| Mastercard Inc. (MA) 1.91% | Mastercard Inc. (MA) 1.91% |
| 41.36% of total net asset | 22.22% of total net assets |
Source: advisors.vanguard.com
The top 10 in both companies are rather similar. However, top 10 companies in VUG makes up almost half of the total asset, whereas in VTI, top 10 only constitutes for 22% of the total.
Sectors
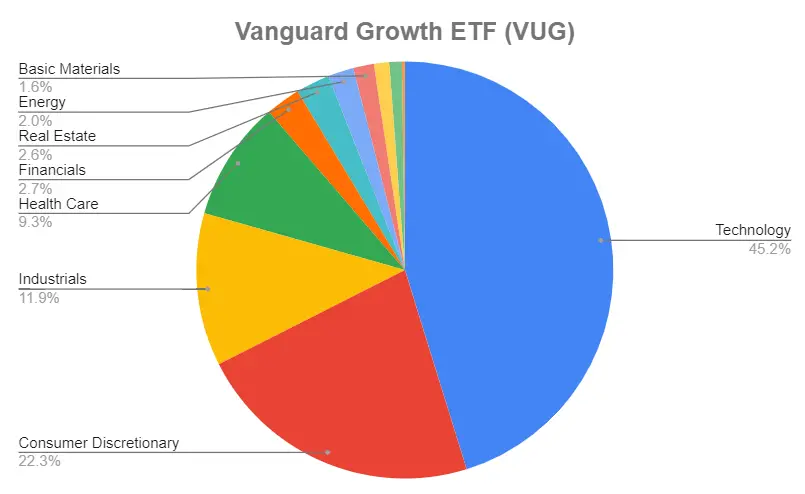
Based on the chart above, we can see that for Technology stocks makes up 45.2% of VUG.
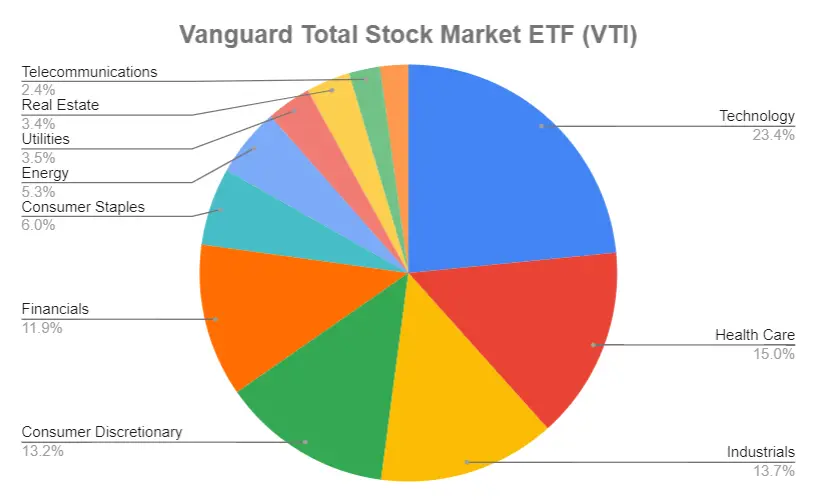
Based on the chart above, we can see that VTI is more balanced in terms of exposures in different sectors
VUG vs VTI – Performance
Using the Portfolio Visualizer to back test these 2 ETFs, we can then compare the portfolio growth between Jan 2005 – Dec 2022. The time period was constrained by the available data for Vanguard Growth ETF.
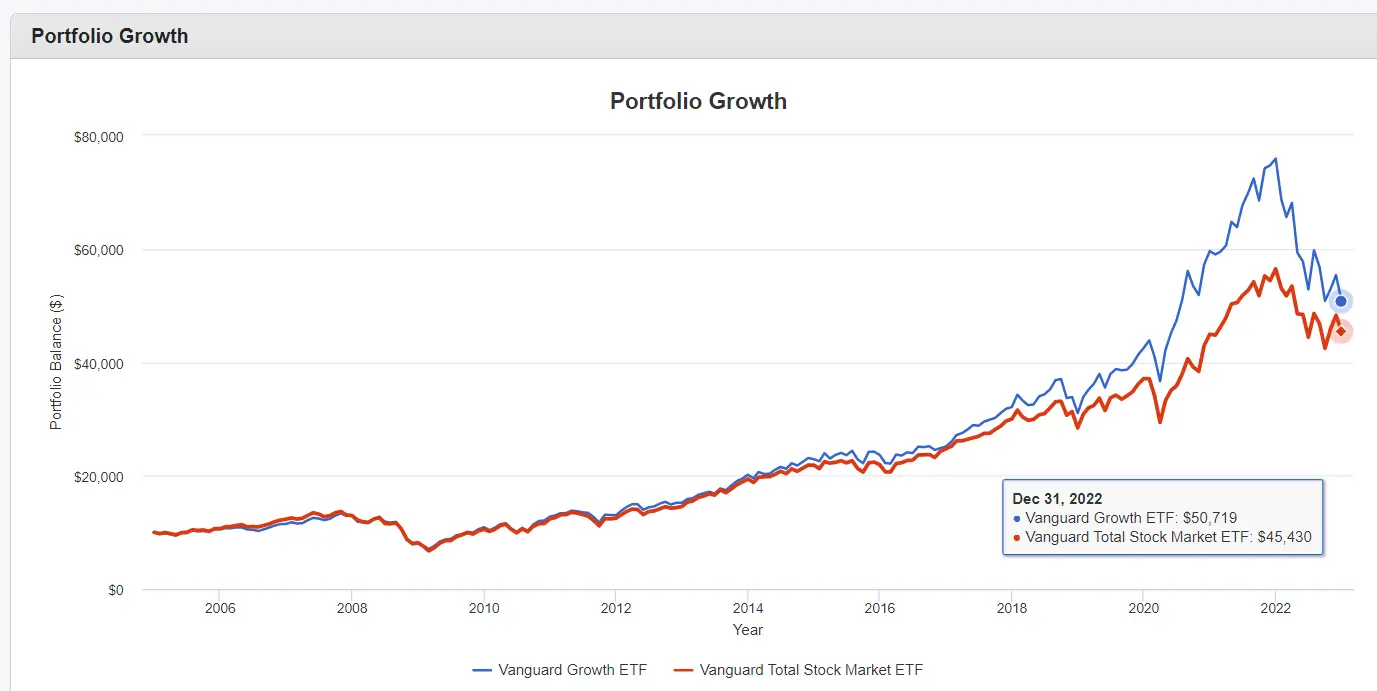
From the graph above, we can see that if we were to invest $10,000 at the start of 2005, we would have ended up with $50,719 for VUG and $45,430 for VTI. This is 11.64% more in terms of growth for VUG.
Has this always been the case where VUG would outperform VTI? I thought it would be interesting to take a closer look at the period leading to the 2009 crash.
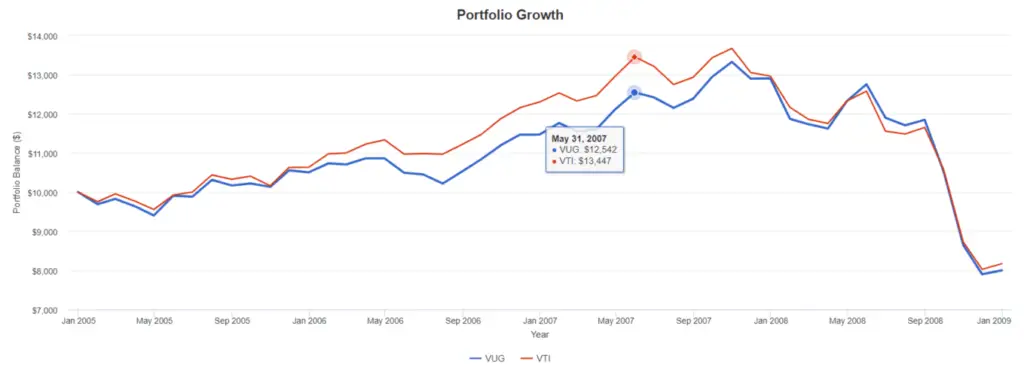
From the graph, we can see that the VTI has outperformed VUG during this period.
Annual Returns
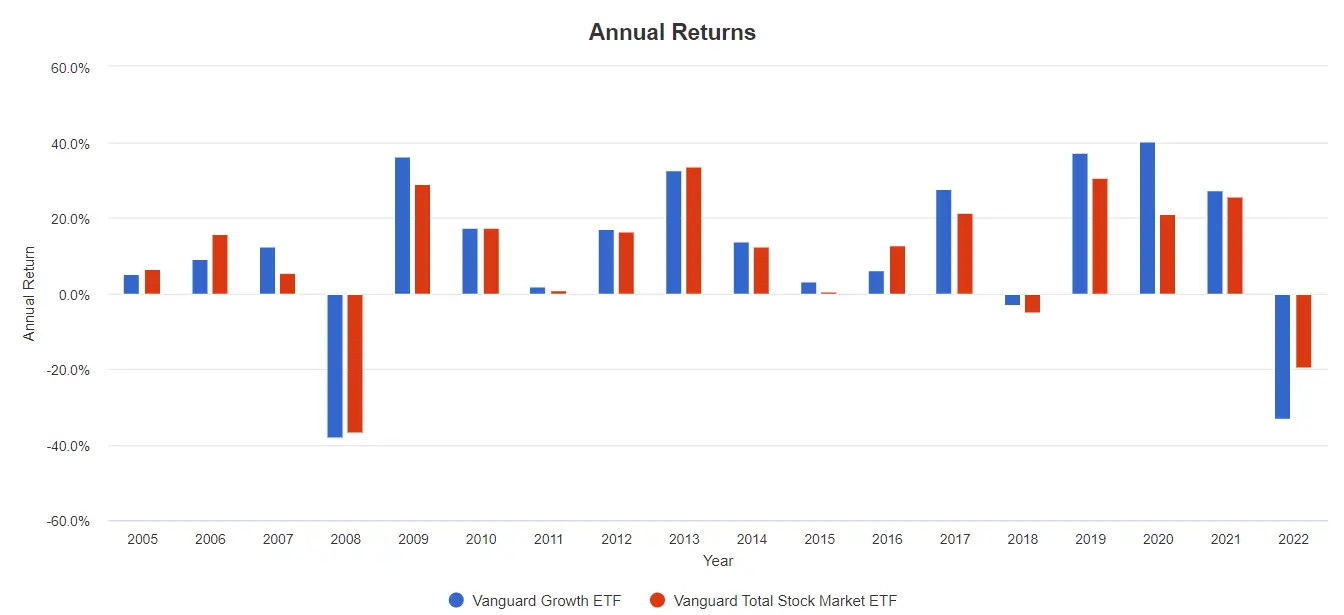
If we look at the above chart for the annual returns between 2005-2022, there are 3 years where the both ETFs has negative return.
| Years that return Negative returns | VUG | VTI |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | -38.02% | -36.98% |
| 2018 | -3.31% | -5.21% |
| 2022 | -33.157% | -19.51% |
In 2008 and 2018, both ETFs perform rather similar. As we all know, tech stocks plummeted in 2022, and VUG had 45.2% of its holdings in tech stocks. This is why VUG performed more poorly when compared to VTI in 2022.
And also, we can see that VTI delivers better returns in only 5 out of the 15 positive return years in 2006, 2010, 2013 and 2016. VUG performs better in 10 out of the 15 positive return years.
Annualized Returns
| 1 Year | 3 Year | 5 Year | 10 Year | Since Inception | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VUG | -33.13% | 6.06% | 9.62% | 12.80% | 9.11% |
| VTI | -19.51% | 6.97% | 8.70% | 12.08% | 7.52% |
Source: advisors.vanguard.com
Which one to go long term with?
Based on past performance, Vanguard Growth ETF seems to be the one to go with. You get a 11.64% more in terms of portfolio growth. But investing in Vanguard Growth means that almost half of your portfolio will be in the tech sector. Are you comfortable with the high concentration of tech stocks in your portfolio?
If you want a more balanced portfolio, then Vanguard Total Market ETF is a better choice, even though it has lesser growth.
But always remember that Past Performance is No Guarantee of Future Results.